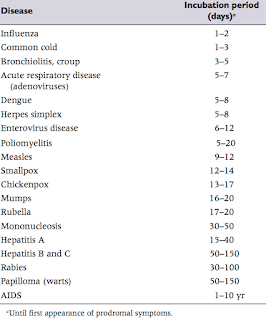
The incubation of a virus is critical as it represents the time a person is contagious. The incubation period is the time between catching an illness and showing symptoms of the illness. With the coronavirus, current estimates suggest that symptoms of COVID-19 usually appear within around five days or less in most cases, but the range could be between 1 and 14 days. This is the reason for the 2-week quarantine everyone hears about.
The virus is NOT going to infect you if:
1. you wash your hand frequently and
2. never touch your face without first good hand hygiene (putting alcohol pumped/washed hands) and
3. never eat without first good hand hygiene (putting alcohol pumped/washed hands) and
4. you do not breathe in or allow your mucus membranes (eyes, nose [lungs], mouth [esophagus], vagina, rectum) to be in contact with contaminated viral droplets (ie, no one coughs in your face or touches your mucus membranes or penetrates you or your skin who is contaminated or with a contaminated instrument.
Some of these can be tough to prevent. If you shake someone’s hand and then to touch your nose, mouth or eyes, you can get any virus that person has on his or her hands, even if that person is not sick. Nose pickers beware!
Hopefully, everyone will practice good hand hygiene:
I think the best way to prevent getting the virus is good hand hygiene which in my book is:
1. Alcholol pump rubbed in between fingers and full hand and ideally if you can
2. Wash off with hot soapy water, especially before eating.
Alcohol pumps and Chlorox wipes outside and inside a sick person’s room helps prevent spreading the virus to the whole family: We wipe down everything we touch in the room and anything the person would have touched–especially doorknobs, banisters, keyboards, light switches, toilet flusher, toothpaste, tissue box in family room….etc.
These viruses can stick around for a while so wipe down everything.
Here is more information for other viruses.
Duration
For viral hepatitis, the incubation period (the time it takes for a
person to become infected after being exposed) varies depending on which
hepatitis virus causes the disease:
- For hepatitis A, the incubation period is 2 to 6 weeks.
- For hepatitis B, the incubation period is between 4 and 20 weeks.
- For hepatitis C, it’s estimated that the incubation period is 2 to 26 weeks.
Hepatitis A is usually active for a short period of time and once a
person recovers, he or she can no longer pass the virus to other people.
It’s practically unheard for people to become chronic carriers of
hepatitis A. Almost all previously healthy persons who develop hepatitis
A will completely recover from their illness in a few weeks or months
without long-term complications.
With hepatitis B, 85% to 90% of patients recover from their illness
completely within 6 months, without long-term complications.
However, 75% to 85% of those who are infected with hepatitis C do not recover completely and are more likely to continue to have a long-term infection. People with hepatitis B (the percentage who don’t recover completely) or hepatitis C who continue to be infected can go on to develop chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver
(the chronic degeneration and disruption of the structure of the
liver). Some people with hepatitis B or C may also become lifelong
carriers of these viruses and can spread them to other people.
The incubation period for herpes is from 2 to 7 days
5.6 days (95% CI 4.8-6.3) for adenovirus,
3.2 days (95% CI 2.8-3.7) for human coronavirus,
4.0 days (95% CI 3.6-4.4) for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus,
1.4 days (95% CI 1.3-1.5) for influenza A,
0.6 days (95% CI 0.5-0.6) for influenza B,
12.5 days (95% CI 11.8-13.3) for measles,
2.6 days (95% CI 2.1-3.1) for parainfluenza,
4.4 days (95% CI 3.9-4.9) for respiratory syncytial virus,
1.9 days (95% CI 1.4-2.4) for rhinovirus
References: