Still, the below result is what I have been seeing in my patients as a reluctant, skeptical surgeon who has been shocked by the numbers of young people who are coming in with dry eye symptoms and meibomian gland atrophy on meibography.
The facts are that aging and screen time appears to worsen meibomian gland scar tissue and atrophy. Doing nothing (like warm compresses, blinking, etc) seems to allow atrophy and scarring to progress. Thermopulsation like Lipiflow, Intense Pulse Light, and Meibomain gland probing seem to delay the progression of atrophy and in some patients help these priceless oil glands to “grow back”/fill up with oil again. I have seen this time and again so a larger randomized controlled study performed in the US is needed with an experienced, meibomian gland probing surgeon, who does not have a financial interest in these procedures.
No studies I could find showed scarring from meibomian gland probing. No studies I could find showed glands worsened after IPL. There are 2 reports I know of severe uveitis after IPL in a patients who were treated without a metal shield over their eyeballs. I have not seen any styes or chalazia after IPL or probing yet, but it has been reported. I have seen 2 patients develop a stye after Lipiflow (likely because the oil is coming out more but the orifice gets clogged with debris, Demodex, dead cells, makeup, etc) but they were able to resolve it with warm compresses and gentle expression.
I have not seen anyone develop an eye infection after any of these procedures.
I have seen many patient who live a life of miser with dry eye disease and are frustrated FDA approved drops such as Xiidra, Restasis, Cequa do not help or make them feel worse.
I think Meibomian Gland probing, Intense Pulse Light, Lipiflow, iLux (though I felt Lipiflow was much less painful than iLux when I had both done at separate times) is safe and effective with little risk.
References:
1. https://bmcophthalmol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12886-019-1219-6
2. https://bjo.bmj.com/content/102/1/59
**
Full article and more references:
1. https://bmcophthalmol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12886-019-1219-6
Clinical results of Intraductal Meibomian gland probing combined with intense pulsed light in treating patients with refractory obstructive Meibomian gland dysfunction: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Conclusions
- Research article
- Open Access
- Published:
Clinical results of Intraductal Meibomian gland probing combined with intense pulsed light in treating patients with refractory obstructive Meibomian gland dysfunction: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Trial registration
Background
Methods
Patient selection and study design
Treatment procedure
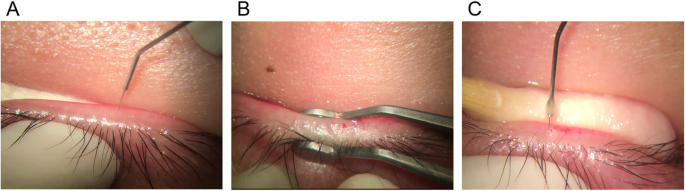
Intraductal meibomian canal probing
Intense pulsed light
Clinical evaluation
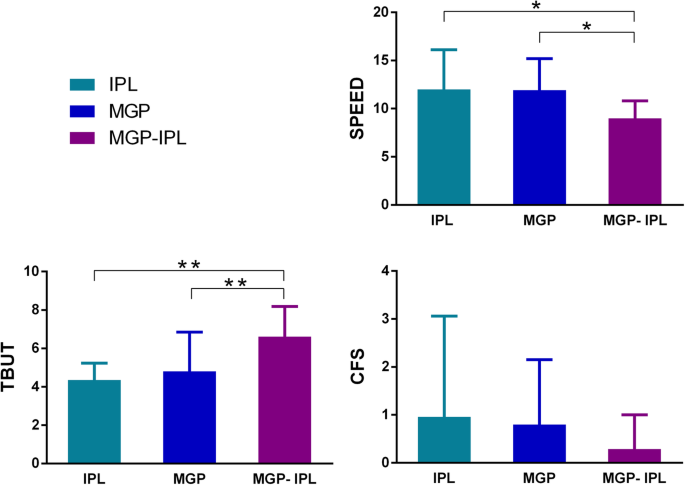
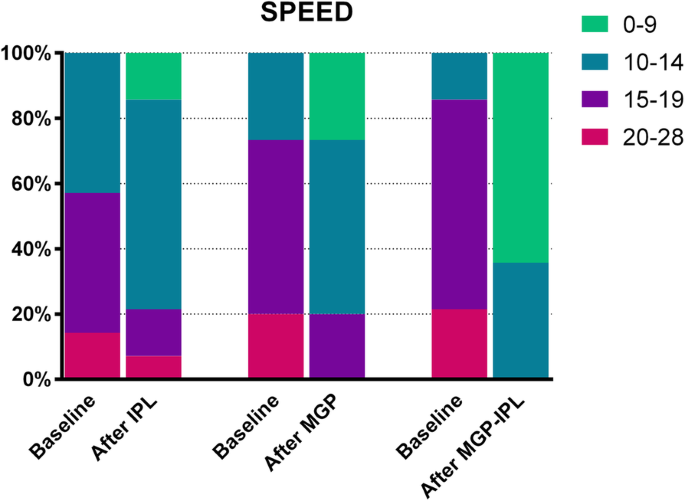
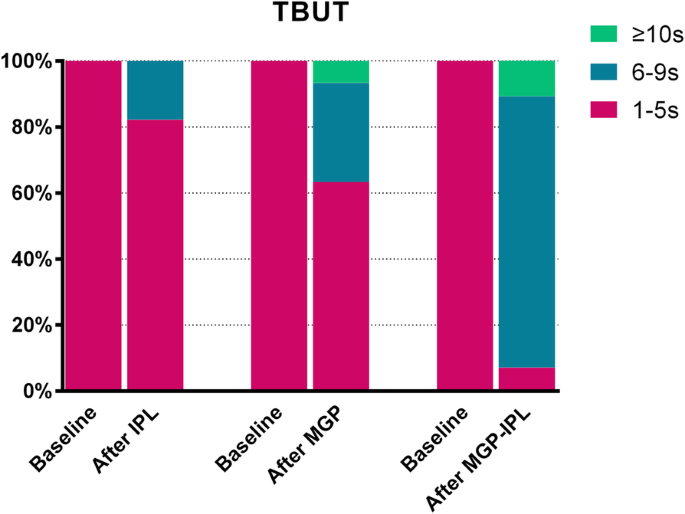
SPEED, CFS and TBUT
Meibum grade
Lid margin finding results
Statistical analysis
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
Availability of data and materials
Abbreviations
- BKC:
-
Blepharon- keratoconjunctivtis
- CFS:
-
Corneal fluorescein staining
- IPL:
-
Intense pulsed light
- IR-M:
-
infrared meibography
- LASIK:
-
Laser Assisted In-situ Keratomi
- MG:
-
Meibomian gland
- MGP:
-
Intraductal meibomian gland probing
- o-MGD:
-
Obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction
- SPEED:
-
Standard Patient Evaluation of Eye Dryness score
- TBUT:
-
Tear break-up time
References
- 1.
Waduthantri S, Yong SS, Tan CH, et al. Cost of dry eye treatment in an Asian clinic setting. PLoS One. 2012;7:e37711. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037711.
- 2.
Miljanovic B, Dana R, Sullivan DA, Schaumberg DA. Impact of dry eye syndrome on vision related quality of life. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007;143:409–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2006.11.060.
- 3.
Nelson JD, Shimazaki J, Benitez-del-Castillo JM, et al. The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: report of the definition and classification subcommittee. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:1930–7. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.10-6997b.
- 4.
Rabensteiner DF, Aminfar H, Boldin I, Schwantzer G, Horwath-Winter J. The prevalence of meibomian gland dysfunction, tear film and ocular surface parameters in an Austrian dry eye clinic population. Acta Ophthalmol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.13732.
- 5.
Foulks GN, Bron AJ. Meibomian gland dysfunction: a clinical scheme for description, diagnosis,classification, and grading. Ocul Surf 2003;1:107–126.
- 6.
Gayton JL. Etiology, prevalence, and treatment of dry eye disease. Clin Ophthalmol. 2009;3:405–12.
- 7.
Goto E, Monden Y, Takano Y, et al. Treatment of non-inflamed obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction by an infrared warm compression device. Br J Ophthalmol. 2002;86:1403–7.
- 8.
Ma X, Lu Y. Efficacy of Intraductal Meibomian gland probing on tear function in patients with obstructive Meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2016;35:725–30. https://doi.org/10.1097/ico.0000000000000777.
- 9.
Arita R, Morishige N, Koh S, Shirakawa R, Kawashima M, Sakimoto T, et al. Increased tear fluid production as a compensatory response to Meibomian gland loss: a multicenter cross-sectional study. Ophthalmology. 2015;122(5):925–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.12.018.
- 10.
Gupta PK, Vora GK, Matossian C, Kim M, Stinnett S. Outcomes of intense pulsed light therapy for treatment of evaporative dry eye disease. Can J Ophthalmol. 2016;51:249–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcjo.2016.01.005.
- 11.
Jiang X, Lv H, Song H, et al. Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of intense pulsed light in the treatment of Meibomian gland dysfunction. J Ophthalmol. 2016;2016:1910694. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1910694.
- 12.
Maskin SL. Intraductal meibomian gland probing relieves symptoms of obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2010;29:1145–52. https://doi.org/10.1097/ICO.0b013e3181d836f3.
- 13.
Sik Sarman Z, Cucen B, Yuksel N, Cengiz A, Caglar Y. Effectiveness of Intraductal Meibomian gland probing for obstructive Meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2016;35:721–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/ico.0000000000000820.
- 14.
Nakayama N, Kawashima M, Kaido M, Arita R, Tsubota K. Analysis of Meibum before and after Intraductal Meibomian gland probing in eyes with obstructive Meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2015;34:1206–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/ico.0000000000000558.
- 15.
Asiedu K, Kyei S, Mensah SN, Ocansey S, Abu LS, Kyere EA. Ocular surface disease index (OSDI) versus the standard patient evaluation of eye dryness (SPEED): a study of a nonclinical sample. Cornea. 2016;35:175–80. https://doi.org/10.1097/ico.0000000000000712.
- 16.
Song X, Zhao P, Wang G, Zhao X. The effects of estrogen and androgen on tear secretion and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression in lacrimal glands of ovariectomized rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(2):745–51. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.12-10457.
- 17.
Lee H, Kim M, Park SY, Kim EK, Seo KY, Kim TI. Mechanical meibomian gland squeezing combined with eyelid scrubs and warm compresses for the treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction. Clin Exp Optom. 2017;100(6):598–602. https://doi.org/10.1111/cxo.12532.
- 18.
Greiner JV. Long-term (3 year) effects of a single thermal pulsation system treatment on Meibomian gland function and dry eye symptoms. Eye Contact Lens. 2016;42(2):99–107. https://doi.org/10.1097/icl.0000000000000166.
- 19.
Jin X, Lin Z, Liu Y, Lin L, Zhu B. Hormone replacement therapy benefits meibomian gland dysfunction in perimenopausal women. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(31):e4268. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000004268.
- 20.
Arita R, Mizoguchi T, Fukuoka S, Morishige N. Multicenter study of intense pulsed light therapy for patients with refractory Meibomian gland dysfunction. Cornea. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1097/ico.0000000000001687.
- 21.
Syed ZA, Sutula FC. Dynamic Intraductal Meibomian probing: a modified approach to the treatment of obstructive Meibomian gland dysfunction. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;33:307–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/IOP.0000000000000876.
- 22.
Maskin SL, Testa WR. Growth of meibomian gland tissue after intraductal meibomian gland probing in patients with obstructive meibomian gland dysfunction. Br J Ophthalmol. 2018;102:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2016-310097.
- 23.
Ashraf Z, Pasha U, Greenstone V, Akbar J, Apenbrinck E, Foulks GN. Quantification of human sebum on skin and human meibum on the eye lid margin using Sebutape(R), spectroscopy and chemical analysis. Curr Eye Res. 2011;36:553–62. https://doi.org/10.3109/02713683.2011.574331.
- 24.
Lee H, Chung B, Kim KS, Seo KY, Choi BJ, Kim TI. Effects of topical loteprednol etabonate on tear cytokines and clinical outcomes in moderate and severe meibomian gland dysfunction: randomized clinical trial. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014;158:1172–1183.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajo.2014.08.015.
- 25.
Liu S, Richards SM, Lo K, Hatton M, Fay A, Sullivan DA. Changes in gene expression in human meibomian gland dysfunction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:2727–40. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.10-6482.
- 26.
Toyos R, McGill W, Briscoe D. Intense pulsed light treatment for dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction; a 3-year retrospective study. Photomed Laser Surg. 2015;33:41–6. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2014.3819.
- 27.
Dell SJ, Gaster RN, Barbarino SC, Cunningham DN. Prospective evaluation of intense pulsed light and meibomian gland expression efficacy on relieving signs and symptoms of dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction. Clin Ophthalmol. 2017;11:817–27. https://doi.org/10.2147/opth.s130706.
- 28.
Bron AJ, Benjamin L, Snibson GR. Meibomian gland disease. Classification and grading of lid changes. Eye. 1991;5(Pt 4):395–411. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.1991.65.
- 29.
Geerling G, Tauber J, Baudouin C, et al. The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: report of the subcommittee on management and treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:2050–64. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.10-6997g.
- 30.
Shine WE, McCulley JP. Polar lipids in human meibomian gland secretions. Curr Eye Res. 2003;26:89–94.
- 31.
Arita R, Morishige N, Shirakawa R, Sato Y, Amano S. Effects of eyelid warming devices on tear film parameters in Normal subjects and patients with Meibomian gland dysfunction. Ocul Surf. 2015;13:321–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtos.2015.04.005.
Acknowledgements
Additional statement
Funding
Author information
Affiliations
Contributions
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Competing interests
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Rights and permissions
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02256969